Social responsibility of business
The social responsibility of business means various obligations or responsibilities or duties that a business-organization has towards the society within which it exists and operates from.
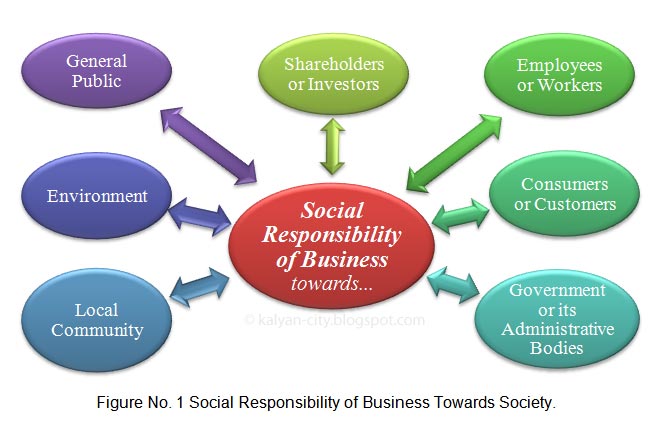
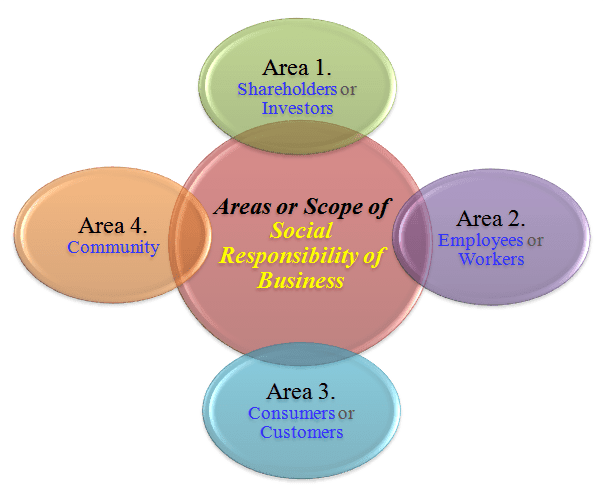
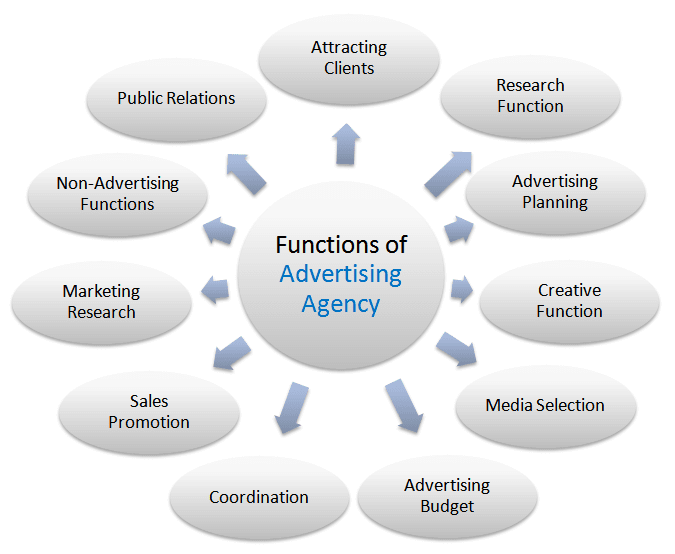
Generally, the social responsibility of business comprises of certain duties towards entities, which are depicted and listed below.
- Shareholders or investors who contribute funds for business.
- Employees and others that make up its personnel.
- Consumers or customers who consumes and/or uses its outputs (products and/or services).
- Government and local administrative bodies that regulate its commercial activities in their jurisdictions.
- Members of a local community who are either directly or indirectly influenced by its activities in their area.
- Surrounding environment of a location from it operates.
- The general public that makes up a big part of society.
The social responsibility of business comprises of the following obligations:
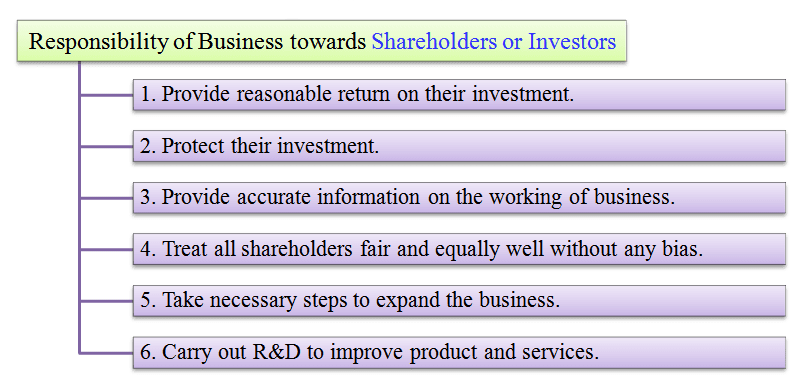
- A business must give a proper dividend to its shareholders or investors.
- It must provide fair wages and salaries with good working conditions.
- It must provide a regular supply of good quality goods and/or services to its consumers/customers at reasonable prices.
- It must abide by all government rules and regulations, supports its business-related policies and should pay fair taxes without keeping any delays or dues.
- It must also contribute in betterment of a local community by doing generous activities like building schools, colleges, hospitals, etc.
- It must take immense care to see that its activities neither directly nor indirectly create a havoc on the vitality of its surrounding environment.
- It should maintain a stringent policy to curb or control pollution in regard to contamination of air, water, land, sound and radiation leakages. Here, to do so, it must hire experienced professional individuals who are experts in their respective fields.
- It should also offer social-welfare services to the general public.
The core objectives of social responsibility of business are as follows:
- It is a concept that implies a business must operate (function) with a firm mindset to protect and promote the interest and welfare of society.
- Profit (earned through any means) must not be its only highest objective else contributions made for betterment and progress of a society must also be given a prime importance.
- It must honestly fulfill its social responsibilities in regard to the welfare of society in which it operates and whose resources & infrastructures it makes use of to earn huge profits.
- It should never neglect (avoid) its responsibilities towards society in which it flourishes.
Now let's discuss, how the survival, growth and success of business are linked and dependent on sincere execution of its social responsibilities.
Note: Refer above figure and try to co-relate articles given in this image with following points of justification.
1. Shareholders or investors
Social responsibility of business towards its shareholders or investors is most important of all other obligations.
If a business satisfies its funders, they are likely to invest more money in a project. As a result, more funds will flow in and the same can be utilized to modernize, expand and diversify the existing activities on a larger scale. Happy financiers can fulfill the rising demand of funds needed for its growth and expansion.
2. Personnel
Social responsibility of business towards its personnel is important because they are the wheels of an organization. Without their support, the commercial institution simply can't function or operate.
If a business takes care of the needs of its human resource (for e.g. of office staff, employees, workers, etc.) wisely, it will boost the motivation and working spirit within an organization. A happy employee usually gives his best to the organization in terms of quality labor and timely output than an unsatisfied one. A pleasant working environment helps in improving the efficiency and productivity of working people. A good remuneration policy attracts new talented professionals who can further contribute in its growth and expansion.
Thus, if personnel is satisfied, then they will work together very hard and aid in increasing the production, sales and profit.
3. Consumers or customers
Social responsibility of business towards its consumers or customers matters a lot from sales and profit point of view. Its success is directly dependents on their level of satisfaction. Higher their rate of satisfaction greater are the chances to succeed.
If a business rolls out good-quality products and/or delivers better quality services that too at reasonable prices, then it is natural to attract lots of customers. If the quality-price ratio is maintained well and consumers get worth for their money spend, this will surely satisfy them. In a long run, customer loyalty and retention will grow, and this will ultimately lead to profitability.
4. Government
Social responsibility of business towards government's regulatory bodies or agencies is quite sensitive from the license's point of view. If permission is not granted or revoked abruptly, it can result in huge losses to an organization. Therefore, compliance in this regard is necessary.
Furthermore, a business must also function within the demarcation of rules and policies as formulated from time to time by the government of state or nation. It should respect laws and abide by all established regulations while performing within the jurisdiction of state.
Some examples of activities a business can do in this regard:
- Licensing an organization,
- Seeking permissions wherever necessary,
- Paying fair taxes on time,
- Following labor, environmental and other laws, etc.
If laws are respected and followed, it creates a goodwill of business in eyes of authorities. Overall, if a government is satisfied it will make favorable commercial policies, which will ultimately open new opportunities and finally benefit the organization sooner or later.
Therefore, satisfaction of government and local administrative bodies is equally important for legal continuation of business.
5. Local community
Social responsibility of business towards the local community of its established area is significant. This is essential for smooth functioning of its activities without any agitations or hindrances.
A business has a responsibility towards the local community besides which it is established and operates from. Industrial activities carried out in a local-area affect the lives of many people who reside in and around it. So, as a compensation for their hardship, an organization must do something or other to alleviate the intensity of suffering.
As a service to the local community, a business can build:
- A trust-run hospital or health center for local patients,
- A primary and secondary school for local children,
- A diploma and degree college for local students,
- An employment center for recruiting skilled local people, etc.
Such activities to some-extend may satisfy the people that make local community and hence their changes of agitations against an establishment are greatly reduced. This will ensure the longevity of a business in a long run.
6. Environment
Social responsibility of business with respect to its surrounding environment can't be sidelined at any cost. It must show a keen interest to safeguard and not harm the vitality of the nature.
A business must take enough care to check that its activities don't create a negative impact on the environment. For example, dumping of industrial wastes without proper treatment must be strictly avoided. Guidelines as stipulated in the environmental laws must be sincerely followed. Lives of all living beings are impacted either positively or negatively depending on how well their surrounding environment is maintained (naturally or artificially). Humans also are no exception to this. In other words, health of an environment influences the health of our society.
Hence, environmental safety must not be an option else a top priority of every business.
7. Public
Finally, social responsibility of business in general can also contribute to make the lives of people a little better.
Some examples of services towards public include:
- Building and maintaining devotional or spiritual places and gardens for people,
- Sponsoring the education of poor meritorious students,
- Organizing events for a social cause, etc.
Such philanthropic actions create a goodwill or fame for the business-organization in the psyche of general public, which though slowly but ultimately pay off in a due course of time.
The world is recognizing the importance of social responsibility of business.
 What is Productivity? Definition ↓
What is Productivity? Definition ↓