Explain Benefits or Importance of Inventory Control
Interdependence of Production and Marketing in Business
What is Debit Card? Definition Meaning
What are Advantages of Debit Card?
Changing Concept of Business from Profit to Environment
What is Advertising? Etymology Definition Meaning of Advertising
Factors Responsible for Changing Concept of Business
Importance of Advertising - Why Advertising is Important?
![square]() Importance of Advertising
Importance of Advertising
The importance of advertising is depicted in the following image.
The significance or importance of advertising in business is as follows:
- Crucial for a launch or announcement.
- Source of revenue for publishers.
- Promotes goods, services, ideas and events.
- Helps in increasing the sales.
- Maximizes the profit of an advertiser.
- Creates consumer awareness.
- Educate society.
- Art, Science and Profession.
- Demands creativity.
- Element of marketing mix.
- Target oriented.
- Use persuasion for results.
- Demands monitoring of demand and supply.
- Builds brand's image.
- Generates employment.
Above points highlighting importance of advertising are discussed below.
![square]() Why Advertising is Important?
Why Advertising is Important?
Now let's find out why advertising is important in business.
1. Crucial for a launch
Advertising is very crucial for launching (introducing) a new product, service and/or idea in the market.
If advertisement of any concerned product, service and/or idea is done properly at a right place, through proper media, and within a specific time constraint, can attract new-customers. This helps to capture the market and increase sales of an advertiser.
Advertising is also essential for announcing an upcoming event.
Advertising an open invitation maximizes the chances of event attendance. However, if people are unaware of any such happening, they may not show up. As a result, the event may not get an expected response.
Hence, advertising contributes to the success of an event.
2. Source of revenue
Advertising is a prime source of revenue for publishers of mass-media like newspapers, TV channels, magazines, websites, etc.
The input cost involved in processing any valuable information is usually higher than its selling price. A publisher's cost rises due to various data gatherings and information-processing activities like research (investigation), professional writing, editing, proof-reading; publishing in form of printing or digital web hosting, and distribution.
Advertising pays publishers their input costs and in return use their media platform as a medium to reach maximum people. Indirectly, because of it, customers of publishers (who are mostly readers and/or viewers) also get an affordable access (or sometimes even a free access) to high-quality information databases.
For example, newspapers sell for pennies, although their input costs are very high. Most online websites give free and unlimited access to their information database for 24X7 because their input costs are mostly recovered from sponsors and ad-networks.
Without support of advertising, the publishing industry (both print and digital media) may not survive.
For example, today, the U.S. newspaper industry is falling deep due to the emergence of online digital media and plummeting demands for print media. Many newspapers in America are either laying off their staff or totally closing down due to major loss of their advertising revenue, which was primarily earned from classified-ads. The availability of free online classified services like Craigslist has compelled many newspapers to either pack up or adapt to new digital age.
3. Sales promotion
Advertising is done to promote goods, services, ideas and/or events.
Advertising is used for the promotion of:
- Goods falling under categories like cosmetics, electronics, eatables, stationary, jewelry, textiles, etc.
- Services provided under banking, insurance, hospitality, air travel, consultancy, health care, education, etc.
- Ideas. For e.g., an entrepreneur encourages general public to invest in his business ideas.
- Events or gatherings like festivals, exhibitions, ceremonies, rallies, etc.
4. Increases sales
Advertising sparks an interest in masses about advertised products and/or services of its advertiser. This interest creates demand in the market. The growing demand soon results in higher sales. Eventually, the advertiser fulfills his main goal of investing in an advertisement.
However, to continue with such a growth in sales, the advertiser must also maintain a good price-quality ratio along with regularly continuing his ad campaigns.
5. Maximizes profit
Advertising helps in increasing sales and control the cost borne by the advertiser. It helps to widen the gap between his sales and incurred cost. With maximizing sales and lowering cost, the profit of a advertiser grows.
Thus, advertising aids in maximizing the profit of its advertiser.
6. Consumer awareness
Advertising creates awareness by informing consumers.
- Awareness : Advertising creates an awareness among consumers about an availability of any specific product and/or service in the market. It attempts to convey them why an advertised product and/or service is better than other alternatives currently available in the market.
- Information : Advertising informs a consumer, mainly about; various features, benefits, price and use of an advertised product and/or service. It also gives information about the brand name or trade-mark used, address of a manufacture or a service provider, and other relevant details to the consumer.
While creating awareness and supplying relevant information, advertising ultimately helps a consumer to make a right choice in his or her purchase.
7. Educate society
Advertising has a remarkable ability to reach masses and educate the society. Therefore, many Governments and even Non-Governmental Organizations (NGO) often take help of advertisements to reach and educate people on important social issues.
Creative ads are made in public interest to educate people about family planning, AIDS awareness, saving water and electricity, giving children compulsory education, providing a right kind of nutrition to mother and her new-born infant, abolishing child labour, etc.
8. Art, Science and Profession
Advertising is all; an art, a science and a profession.
Advertising is:
- Art because it needs creative skills.
- Science because it depends on systematic and scientific planning.
- Profession because it's done by professional agencies who follow certain business ethics or a code of conduct.
9. Demands creativity
Advertising is impossible without creative thinking. In other words, creativity is the essence (main ingredient or soul) of advertising.
For an advertisement to be a success, it must have some fundamental aspects or characteristics in it.
An advertisement (ad) must be:
- Creative,
- Original,
- Not a copied one,
- Artistic, and also
- Attractive to large masses.
To make advertisements more creative and appealing, professional ad-agencies must hire people with creative minds. Preference must be given to those who think Out of the box and are always ready with their newer concept, jingles, and innovative presentations.
Hello Honey Bunny is a good example of a creative ad.
In India, Idea Cellular Ltd. (A mobile service provider) launched an ad-campaign called Hello Honey Bunny. This ad was cute, kiddy like, and so addictive that it quickly went viral.
10. Element of marketing mix
Advertising is an important element of marketing mix. It supports sales promotion.
In today's competitive world, it is getting difficult to sale something. Consumers now-a-days are more cautious and better aware about things they buy and use. They don't easily break their loyalty towards their favourite goods and/or service unless and until somethings allure them in unique way and compells them to atleast give a try.
It is rightly said,
What they (people) often see and hear; it attracts them, allure their psyche to change their preferences, if it holds them and makes them think consciously, this seems trustworthy; it SELLS.
Developing such a level of attraction is possible only with creative ads and that's the reason why many manufacturers are ready to spend huge money on advertising.
11. Target oriented
Advertising is target-oriented in nature. Target oriented means to focus on (or target one's attention to) only a specific thing, at one time.
In context of advertising, it means to focus on (target), or deliver attention towards, only a specific group or class of consumers.
For example, AUDI (German luxury car maker) designs and targets its premium cars to suite comforts, needs, expectations and demands of a rich elite class. In contrast, Maruti Suzuki (Indian car manufacture) mainly targets its fuel-efficient sedan cars to a majority of middle-class groups.
Advertising is effective only if it is focused or target oriented.
12. Persuasion for results
Advertising use persuasion to make people act in the desired direction.
Generally, people are persuaded to:
- Purchase (buy) products and/or services,
- Invest in ideas,
- Attend events, etc.
The persuasion works in the following six stages:
- Give a creative and compelling presentation of a key message.
- Grasp people's attention, repeat exposure and stimulate their senses for a quicker recognition.
- Give comprehension on value (importance) of the message.
- Gain acceptance (belief) of the message.
- Make a possible encounter and easy identification (retention).
- Change people's behavior and let them act (give result) as expected.
13. Monitor demand and supply
Advertising, if done repetitively, helps in generating higher demand in the market for advertised products and/or service. Rising demand must be met with an equivalent amount of supply of products and/or efficient delivery of services. Proper care must be taken to monitor the demand and supply function, so that none of the demands are skipped.
If supply is not made at par with an increasing demand, the market may soon lose confidence and downfall of demand may take place. If this happens, the sale will fall down, and money spent on advertising may not be recovered. This may add to losses.
Thus, when advertising results in higher demands, an appropriate supply must be also ready to compensate it. To see that such compensation is done properly, the demand and supply function must be well monitored.
14. Builds brand's image
Advertising creates goodwill and helps in building a brand's image in the market.
Repeated advertisements makes brands very popular. Generally, people tend to show a more trustworthy attitude towards advertised brands over non-advertised ones. Well-known branded products are usually made from high-quality raw-materials and hence are always preferred by most consumers. This increases demand for such products.
Rise in popularity and building trust gradually helps to increase the value of the brand. This eventually boosts sales of such branded products. It also increases the reputation of that entity who owns these brands.
15. Generates employment
Advertising agencies are constantly in search of newer creative ideas to cope with the rising demands from their clients (advertisers). Each ad assignment (project) demands a high-level of mental labour. There are dead lines within which projects must be completed and submitted. Furthermore, the concept of ad must be also welcomed (approved) by the advertiser. Overall, this creates a huge demand of creative people and thus opens new employment opportunities in the field of advertising.
Advertising provides employment to deserving candidates who are mainly creative thinkers, directors, artists, graphic designers, sales representatives and managers.
Features of Marketing Information System MIS
![square]() Features of Marketing Information System MIS
Features of Marketing Information System MIS
The main characteristics or features of Marketing Information System (MIS):
Image credits © Prof. Mudit Katyani.
- Continuous system : MIS is a permanent and continuous system of collecting information. It collects information continuously.
- Basic objective : The basic objective of MIS is to provide the right-information at the right-time to the right-people to help them take right decisions.
- Computer based system : MIS is a computer-based system. It uses computers for storing, analyzing and supplying information. It also uses micro-films for storing information. Therefore, it is very quick and accurate.
- Future-oriented : MIS is future-oriented. It provides information for solving future problems. It is not past-oriented.
- Used by all levels : MIS is used by all three levels of management, i.e. top, middle and lower. It is used for making marketing plans, policies and strategies. This is used to solve marketing problems and to take advantage of business opportunities.
- Sources : MIS collects information from both, internal and external sources. For example, information is collected from company records, publications, etc.
- Collects marketing information : MIS collects all types of marketing information. It collects information about the consumer competition, marketing environment, government policies, etc. It supplies this information to the marketing managers.
- Helps in decision making : MIS supplies up-to-date and accurate information. It helps marketing managers to take quick and right decisions.
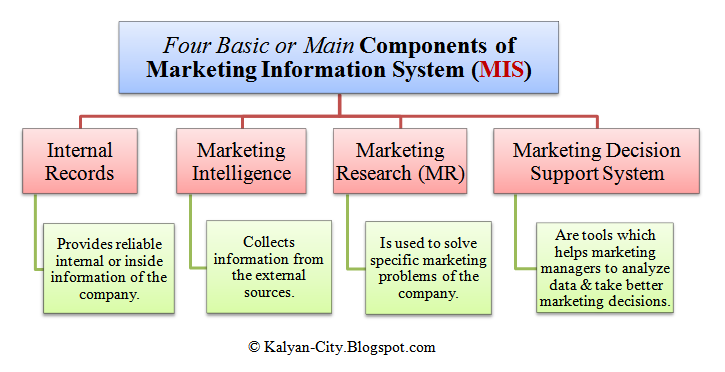
4 Main Components of Marketing Information System (MIS)
![square]() Components of Marketing Information System MIS
Components of Marketing Information System MIS
Marketing Information System (MIS) collects, analyses, and supplies a lot of relevant information to the marketing managers. It is a valuable tool for planning, implementing and controlling the marketing activities.
The role of MIS is to identify (find out) what sort of information is required by the marketing managers. It then collects and analyzes the information. It supplies this information to the marketing manager at the right time. MIS collects the information through its subsystems. These subsystems are called components.
The four main components of Marketing Information System (MIS) are:
- Internal Records,
- Marketing Intelligence,
- Marketing Research (MR), and
- Marketing Decision Support System.
The basic components of MIS are depicted and explained below.
Image credits © Prof. Mudit Katyani.
- Internal records : The first component of MIS is ‘Internal Record’. Marketing managers get lots of information from the internal-records of the company. These records provide current information about sales, costs, inventories, cash flows and account receivable and payable. Many companies maintain their computerized internal records. Inside records help marketing managers to gain faster access to reliable information.
- Marketing intelligence :
- The second component of MIS is ‘Marketing Intelligence’. It collects information from external sources. It provides information about current marketing-environment and changing conditions in the market. This information can be easily gathered from external sources like; magazines, trade journals, commercial press, so on. This information cannot be collected from the Annual Reports of the Trade Association and Chambers of Commerce, Annual Report of Companies, etc. The salesmens report also contains information about market trends.
- The information which is collected from the external sources cannot be used directly. It must be first evaluated and arranged in a proper order. It can be then used by the marketing manager for taking decisions and making policies about marketing.
- So, marketing intelligence is an important component of MIS.
- Marketing research : The third important component of MIS is ‘Marketing Research’. MR is conducted to solve specific marketing problems of the company. It collects data about the problem. This data is tabulated, analyzed and conclusions are drawn. Then the recommendations are given for solving the problem. Marketing research also provides information to the marketing managers. However, this information is specific information. It can be used only for a particular purpose. MIS and MR are not substitutes of each other. The scope of MIS is very wide. It includes ‘MR’. However, the scope of MR is very narrow.
- Marketing decision support system : The fourth component of MIS is ‘Marketing Decision Support System’. These are the tools which help the marketing managers to analyze data and to take better marketing decisions. They include hardware, i.e. computer and software programs. Computer helps the marketing manager to analyze the marketing information. It also helps them to take better decisions. In fact, today marketing managers cannot work without computers. There are many software programs, which help the marketing manager to do market segmentation, price fixing, advertising budgets, etc.
Essential Requisites of a Good MIS
Essential Requisites of a Good MIS
The following image depicts the eight essential requisites of a good MIS.
Image credits © Prof. Mudit Katyani.
The essentials of a good Marketing Information System (MIS) is listed below:
- MIS must be unified and centralized.
- It must facilitate decision making.
- It must provide quick and accurate information.
- It must be economical.
- It must be selective.
- It must be future oriented.
- It must supply information regularly.
- It must use new techniques.
Now let's discuss and find out, “How a good MIS must be?”
- Unified and centralized : MIS must be unified and centralized. It collects and stores different types of market information. All of this information must be unified and centralized. That is, all the marketing information must be brought together (unified) and kept at one central place (centralized). So, it must be at the central-office. This will result in easy access and quick reference. The managers will be able to find all the required information at one place.
- Facilitate decision making : MIS must facilitate decision making. That is, it must guide the marketing managers in decision making. It must provide required information to the managers to help in taking decisions. This information must be of a good quality. That is, it must be relevant, reliable, and up-to-date. This will result in an accurate decision-making process. So, it must not only be a data bank. It must play a positive role in the decision-making process.
- Quick and accurate information : MIS must provide quick and accurate information. Today, managers have to take quick-decisions because the marketing is moving very fast. If they don't take quickest decisions, then they will lose many marketing opportunities. Therefore, it must provide quick information to the managers. This information must also be accurate, regular and continuous. It must be a user-oriented one. It must collect, classify, verify, store and supply information quickly and accurately.
- Economical : MIS must be economical. That is, it must not be very costly. The expenditure on it must be minimum. It must not exceed its value. It must give maximum benefits to the company at a minimum cost. It will be economical only if it is selective. It must be particular in collecting, analyzing, storing and supplying information. It must use a minimum number of employees in its operation. It must be economical because it is not directly productive. It is a service and support function.
- Selective : MIS must be selective. That is, it must not collect all the market information. It must only collect relevant information. It must collect information, which is very essential and useful for decision making. If it is not selective there will be a waste of time, energy, storage space and money.
- Future oriented : MIS must be forward looking i.e. future-oriented. It must not be a past-oriented one. It must give more importance to future-oriented information. It must provide information for solving problems, which may come up in the future. The company will be successful if their marketing managers are future-oriented. The marketing managers can be so only if the MIS is also future oriented.
- Supply information regularly : MIS must supply information regularly. The business environment is changing constantly. So, the marketing managers have to take marketing decisions continuously. Therefore, they require a regular and continuous flow of market information. This information must be provided by MIS. So, it must supply information regularly to the marketing managers.
- Use new techniques : MIS must use new techniques for collecting, analyzing, storing and supplying information. It must use computers and micro-films. It must use new communication techniques. It must also make the use of the Internet and latest software programs. These newer techniques will increase the efficiency and accuracy of MIS. MIS will also become more economical by using new techniques.
Distinguish Between MIS and Marketing Research (MR)
Distinguish Between MIS and Marketing Research (MR)
Following image depicts the ten main points which are used to make a comparison or distinction between MIS and Marketing Research (MR).
Image credits © Prof. Mudit Katyani.
Difference between MIS vs MR is based on the following ten points:
- Meaning of MIS and MR.
- Their basic or main purpose.
- Wide or narrow scope.
- General or specific nature.
- Number of reports provided.
- Future or past orientation.
- Frequency of data collection.
- Number of problems to solve.
- Continuous or non-continuous operational method.
- Based on use of computers or not.
Now let's distinguish MIS and Marketing Research (MR) on above points.
- Meaning :
- MIS means to collect, analyze and supply relevant marketing information to the marketing managers. The marketing managers use this information for taking effective marketing decisions. It is a permanent and continuous process.
- Marketing Research (MR) is a systematic process of collecting and analyzing information to solve a specific marketing problem.
- Purpose :
- The main purpose of MIS is to provide relevant information to marketing managers and enable them to make effective marketing decisions.
- However, the main purpose of Marketing Research (MR) is to solve a specific marketing problem.
- Scope :
- The scope of MIS is wide. Marketing Research (MR) is one of its component. It is not only used to solve problems but also helps to prevent problems in the future.
- The scope of Marketing Research (MR) is narrow. It is one small part of MIS. It solves a specific present marketing problem.
- Nature :
- MIS is more nonspecific or general in nature. It can solve many types of marketing problems.
- Marketing Research (MR) is more specific or particular in nature. At one time, it can only solve a single type of marketing problem.
- Reports :
- MIS gives four types of reports namely, plan-reports, periodic-reports, triggered-reports and demand reports.
- Marketing Research (MR) provides only one report called as ‘MR Report.’
- Orientation :
- Orientation of MIS is more future-oriented when compared to MR.
- However, the orientation of Marketing Research (MR) is more past and present one when compared to MIS. It concentrates more on earlier and latest information. It uses this information to solve a current marketing problem.
- Problems :
- MIS deals with and attempts to solve many different marketing problems at one time. For this, it collects, stores, analyze and supply relevant market information to the marketing managers.
- Marketing Research (MR) only deals with a single marketing problem at one time. It doesn't solve multiple marketing problems simultaneously.
- Data :
- In MIS, the data is collected more frequently, usually almost daily. This is a must for every company.
- In Marketing Research (MR), the data is not collected as frequently as MIS. It is collected on a required basis.
- Operation :
- MIS is a permanent and continuous system. Here, the inflow of market information never stops. Data is constantly collected and stored for further analysis. It is properly analyzed, studied and well-organized before supplying to the marketing managers. MIS has a starting but no ending point.
- Marketing Research (MR) is not a continuous system. Here, data is collected only when a company faces a specific marketing problem. It has a starting and ending point.
- Computers :
- MIS is heavily based on the use of computers. Here, computing technologies are widely used to ease and facilitate data collection, its storage, analysis, retrieval and supply of relevant information to marketing managers of the company.
- Unlike MIS, Marketing Research (MR) hardly makes use of computers. It uses computers only for analyzing some information and is not entirely based on computing technologies.
What is Marketing Audit? Definition Meaning
Definition of Marketing Audit
The definition of marketing audit as stated by Abe Schuchman is as follows:
“Marketing audit is a systematic, critical and impartial review and appraisal of the total marketing operation: of the basic objectives and polices and the assumptions which underlie them as well as the methods, procedures, personnel and organization employed to implement the policies and achieve the objectives.”
Abe Schuchman gave this definition of marketing audit in his writings on its first extended discussions. He wrote this discussion for the American Marketing Association (AMA) in 1951.
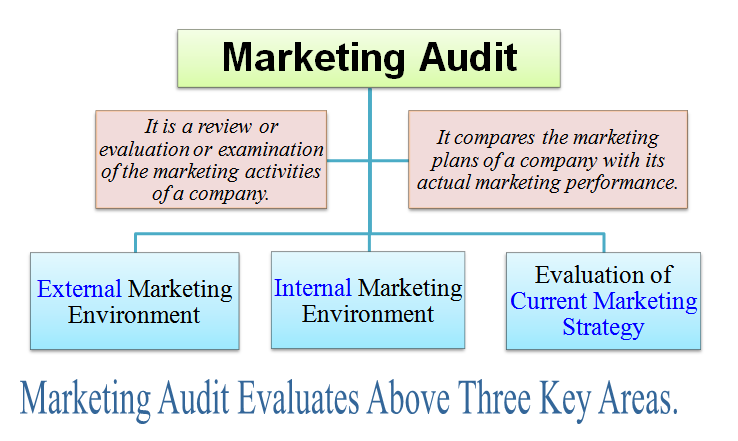
Meaning of Marketing Audit
The meaning of marketing audit is depicted in the following chart.
Marketing audit is an analysis, examination, review or evaluation of marketing activities of a company. It evaluates marketing environment, objectives, plans, policies and strategies of a company. After evaluation, it identifies various defects, vulnerabilities, deficiencies, problems, and other weaknesses encountered in the company's marketing activities. It suggests measures and/or recommendations to overcome, solve or remove these limitations. It also seeks out new marketing opportunities for a company. Overall, it tries to enhance (improve) the marketing performance of a company.
Marketing audit is an extensive, systematic, independent and regular examination process of a company's marketing activities.
- It is an extensive or comprehensive process because it covers all (entire) marketing activities of a company.
- It is a systematic or methodical process since it strictly follows all involved steps or procedures properly.
- It is an independent or autonomous process conducted by an external person. This person is not from the marketing department of a company.
- It is a periodic process because it is conducted continuously after some fixed interval of time.
Marketing audit is very beneficial for the success of a company. It examines, “How well the marketing department of a company works or functions.” It compares the marketing plans of a company with its actual marketing performance. It finds out the strengths and weaknesses of a company's product. It suggests measures to remove the product's weaknesses. It guides a company to adapt its marketing strategies with the changing marketing environment. It helps a company to update its marketing strategies and control its marketing expenses. In short, a company cannot survive without conducting a proper marketing audit.
Additional topics on marketing audit are continued in the following articles:
- Characteristics of marketing audit.
- Types of marketing audit.
- Methods of conducting a marketing audit.
Marketing audit evaluates the following three main (key) responsible areas:
- External marketing environment : Here, the marketing audit mainly focuses on customers and competition in the business.
- Internal marketing environment : Here, the marketing audit studies the structure of company's marketing team and its effectiveness.
- Evaluation of current marketing strategy : Here, the marketing audit continuously reviews current marketing strategy of a company. It also takes help of lessons learned from its past marketing plans.
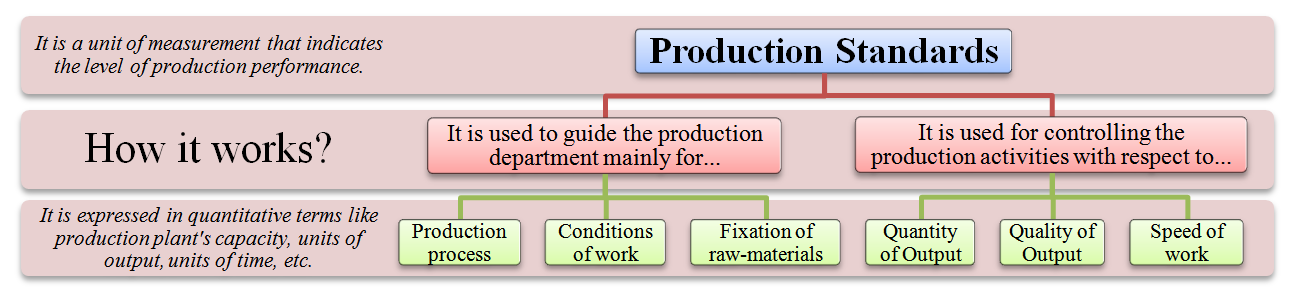
Production Standards Meaning Definition Advantages Demerits
Meaning of Production Standards
Production standard is a criterion or yardstick or benchmark. It is used for measuring the production of the company.
Production standards are fixed for raw materials, production process, tools and equipment, workers, conditions of work, speed of work, quantity of output, quality of output, etc.
Production standards are mostly expressed in quantitative terms. That is, it is expressed in terms of units of output, units of time, kilograms, plant capacity, so on.
Production standards give direction and guidance to the production department. It is also used for controlling the production activities. That is, the actual production can be compared with the production standards, and the difference can be found out and corrected. It is a point of reference. It helps to find out whether the work was done as per plan.
Image credits © Prof. Mudit Katyani.
Definition of Production Standards
According to Adam and Elbert, production standard is defined as follows:
"Production standard is a quantitative criterion established as a basis for comparison in measuring or judging output."
Advantages of Production Standards
The merits, benefits, or advantages of production standards are as follows:
- Optimum use of labour.
- Fixing wages.
- Basis for promotion and training.
- Customer satisfaction.
- Less wastage.
- Budgeting possible.
- Effective planning.
Now let's discuss each advantage of production standards one by one.
1. Optimum use of labour
If production standards are fixed beforehand, then all the work will be planned in advance So, everyone will know exactly what to do, how much to do, how to do it, etc. The performance of the workers can be evaluated. Their mistakes, if any, can be corrected in time. There will be no wastage of labour. So, production planning helps to make optimum use of labour.
2. Fixing wages
Production standards help to fix the wages, salaries, bonus, perks, etc. of the workers and managers. The performance of each person can be evaluated with the help of production standards. So, each person will be paid according to his performance.
3. Basis for promotion and training
Production standards can be used as a basis for giving promotion, transfers, training, etc., to the employees and managers. This is because it helps to evaluate their performance. The employees having the best performance can be given promotions. The employees whose performance is bad can be sent for training to improve their performance.
4. Customer satisfaction
Production standards help to give satisfaction to the consumers. This is because production standards are fixed for quantity, quality, time, cost, etc. So, the consumers will get a regular supply of good-quality products at low prices. This will give satisfaction to the customers and profits to the company.
5. Less wastage
Production standards help to reduce the wastage of human, material and financial resources in the company. This is because standards are fixed for almost everything in the production department. There are standards for raw materials, workers, speed of work, quantity of work, quality of work, production process, etc. These standards guide the workers. It helps them to avoid mistakes. After they complete their work, it is compared with the standards. The mistakes, if any, are found out and corrected in time. Production standards help to avoid wastage of investment in unwanted machines and raw materials. It also helps to avoid having more employees than necessary. All this helps to reduce wastage in the company.
6. Budgeting possible
Production standard makes budgeting possible. That is, the production manager can prepare a budget for all the production expenses. He can prepare a budget for the materials' costs, labour costs, machine costs, repair and maintenance costs, etc. This will help to avoid wastage and to reduce the production cost. It will also reduce financial problems in the organization.
7. Effective planning
Production standards are the base of production planning. It helps to have effective production planning. Production planning helps the production to run smoothly. It sees that all the machines are utilized fully. It helps over and under stocking of materials and finished goods. It helps to deal with emergencies like the breakdown of machines.
Demerits of Production Standards
The limitations, disadvantages, or demerits of production standards are:
- Limiting factor.
- No improvement.
- Individual difference not considered.
- Difference in job methods.
- Rigidity.
Now let's discuss each demerit of production standards one by one.
1. Limiting factor
Some experts feel that a standard is a limiting factor. A standard is a quantitative goal. Once the employee achieves this goal he will be satisfied. He will not try to work more than the standard. He will not try to increase the standard. After some time, he will become lazy.
2. No improvement
Standard are fixed for quantity, time, costs, etc. These standards are not changed for a long period of time. So, during this time the quantity of output, quality of output, speed of work, cost of production, etc., will remain the same. There will be no improvement. This is against Kaizan. Kaizan is a Japanese concept. According to this concept, there must be continuous improvements in the organisation.
3. Individual difference not considered
Standards do not consider individual difference in doing work. The same standard is made for all the employees. However, all the employees are not equally efficient in their work. So, if the standard is made too high, then the less-efficient employees will not be able to complete their work in time. Similarly, if the standards are low, efficient employees will complete their work before time.
4. Difference in job methods
Methods of doing the job are not always standardized. Most companies change their methods according to change in machines. It is difficult to fix standards if the job methods go on changing. Even if standards are fixed, comparisons become hard due to change of methods.
5. Rigidity
Standards are not changed regularly. This results in rigidity. However, flexibility is required to face competition. The product must be changed regularly as per the varying needs and wants of the consumers.
Explain the Characteristics of Marketing Audit
Explain the Characteristics of Marketing Audit
The eight important characteristics of marketing audit are depicted below.
The salient features or characteristics of marketing audit are as follows:
- Marketing audit is a comprehensive study of all marketing activities.
- It is a systematic-process that follows a step-by-step procedure.
- It is a periodic activity and must be conducted regularly.
- It is conducted by an independent person who is not from company.
- It is a critical review of marketing activities of company.
- It is an evaluation of marketing activities of company.
- It finds out marketing opportunities and weaknesses of company.
- It is a preventative and curative marketing medicine.
Now let's briefly discuss or explain each characteristic of marketing audit.
1. Comprehensive study
Marketing audit is a comprehensive or complete study of all the marketing activities of company. It studies the marketing environment, marketing objective, marketing plans, policies and strategies, etc.
2. Systematic process
Marketing audit is a systematic process. It follows a step-by-step procedure.
- It studies marketing environment.
- It studies the internal marketing system.
- It examines the marketing activities.
- It finds out the problems.
- It makes an action plan to remove the problems.
The main aim of marketing audit is to improve the effectiveness of marketing.
3. Periodic activity
A company must conduct a marketing audit regularly or periodically. It must conduct the marketing audit even if it has no problems. This is because it helps the company to analyze the post performance and to make future marketing strategies.
A company must not conduct a marketing audit only if it has problems or when it suffers a loss. It must be a compulsory and not an optional activity.
Marketing audit is like a postmortem of failure.
4. Independently conducted
Marketing audit is independent. That is, it is conducted by an autonomous person. It is not conducted by a person who is working in the marketing department. Mostly, it is conducted by an outside agency.
5. Critical review of marketing activities
Marketing audit is a critical review of marketing activities of the company. It finds out the defects, deficiencies, problems and weakness in company's marketing activities. It also gives suggestions about how to remove these defects or deficiencies.
6. Evaluates marketing activities
Marketing audit is an explanation or evaluation of marketing activities of company. It evaluates company's objective, plans, policies, programs, etc.
7. Finds out opportunities and weaknesses
Marketing audit finds out the marketing opportunities and weakness of the company. It helps the company to take advantage of the marketing objectives. It also helps the company to remove all its weakness.
8. Preventative and curative marketing medicine
Marketing audit is a preventative and curative marketing medicine. It prevents marketing problems. It also cures (solves) marketing problems.
Scope, Areas or Types of Marketing Audit
Scope, Areas or Types of Marketing Audit
There are no fixed guidelines regarding the scope, areas or types of marketing audit. In other words, the scope of marketing audit is not fixed. It changes from company to company. Each company can make its own marketing audit plan. However, the scope of marketing audit must include the following areas or types:
The six important types of marketing audit are:
- Marketing Environment Audit.
- Marketing Strategy Audit.
- Marketing Organization Audit.
- Marketing Systems Audit.
- Marketing Productivity Audit.
- Marketing Function Audit.
Now let's discuss each main area or type of marketing audit.
1. Marketing Environment Audit
Marketing Environment Audit consists of the external environment of company. It includes natural environment, economic environment, political environment, demographic environment, etc. The marketing audit analyses the marketing consumer, competitors, suppliers, so on. This audit helps the company to make marketing strategies.
2. Marketing Strategy Audit
Marketing Strategy Audit is a critical analysis of marketing objectives and strategies. It finds out whether the company's marketing objectives are clear and proper. It also examines the marketing strategies of the company. This audit is done to find out the utility of the marketing strategies.
3. Marketing Organization Audit
Marketing Organization Audit is a systematic study of the company's organizational resources like manpower, organization, structure, employee training and development, Research and Development facilities, motivation, communication and working relations.
4. Marketing Systems Audit
Marketing Systems Audit finds out the company's ability of collecting and analyzing data. It looks for the company's ability to plan and control the marketing activities. It also studies the company's marketing information system, planning and control system, etc.
5. Marketing Productivity Audit
Marketing Productivity Audit finds out the profitability of the company's products. It examines the markets. It also examines the measure to improve cost-effectiveness.
6. Marketing Function Audit
Marketing Function Audit is a complete study of marketing functions in relation to the product, price, promotion and place of distribution. So, it is an audit of the marketing mix (4 P's) of the company.
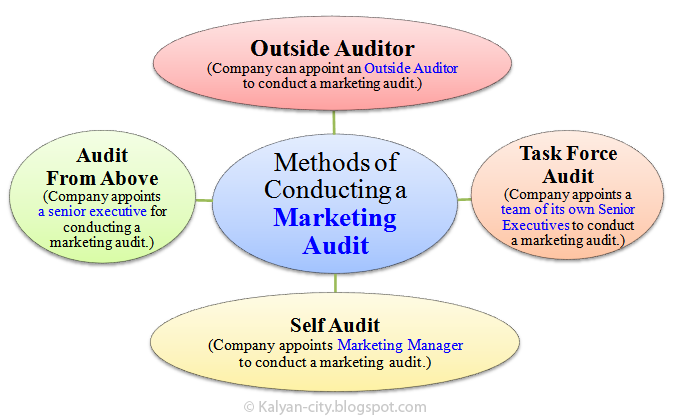
Methods of Conducting a Marketing Audit
Methods of Conducting a Marketing Audit
Marketing audit is an examination of the marketing activities of company. It must be conducted by impartial persons.
Auditors must be properly qualified, trained and experienced enough to do the audit. They must have a complete knowledge and exposure of marketing.
Image below depicts the methods of conducting a marketing audit.
Following methods are used to conduct a marketing audit:
- Outside auditor : Company appoints an outside auditor to conduct a marketing audit.
- Task force audit : Company selects a team of its own senior executives to conduct a marketing audit.
- Self audit : In this method, marketing manager of a company conducts a marketing audit.
- Audit from above : Here, a senior executive of company (for example, a Director) is appointed to conduct a marketing audit.
Now let's discuss, “How is marketing audit conducted?”
1. Outside auditor
In this method, the company can appoint an outside auditor to conduct a marketing audit. An outside-auditor must be professional, a consultant or an agency.
Outside auditors conduct marketing audits for many companies. They have enough skills and experience. They are also more independent, impartial and objective oriented. They give good suggestions for improvement.
Therefore, it is better to use an outside auditor.
Auditor studies information and submits a report to the company. The company has to pay him fees for his services.
2. Task force audit
In ‘Task Force Audit’ method, the company appoints a team of its own executives for conducting a marketing audit. These executives are highly experienced. They conduct the marketing audit independently. They submit their report to the top level of management.
3. Self audit
In ‘Self Audit’ method, the company appoints the marketing manager to conduct a marketing audit. Here, the marketing manager has to conduct a marketing audit himself. This is called self-audit. He has to critically-examine the marketing performances. He has to find out the plus and minus points. Then he has to submit his report to top level of management.
Self audit must be conducted impartially by the marketing manager.
4. Audit from above
In ‘Audit From Above’ method, the company appoints a senior executive to conduct a marketing audit. This executive is mostly a director or a person who has complete knowledge about marketing. This is a type of internal audit.
It is always better to use an outside auditor for conducting a marketing audit. Internal methods have many limitations and hence must be avoided.
Standards Required at Various Levels of Production
Standards Required at Various Levels of Production
Standards are fixed at various levels of production. This is done to ensure some minimum expected output in the production process. Standards are established to maintain a production efficiency. These help to optimally utilizing various factors of production and achieve some fixed amount of output in terms of both; quality and quantity.
Important standards required at various levels of production are listed below.
- Individual Standards.
- Departmental Standards.
- Plant Standards.
Following points discuss these standards in detail.
1. Individual Standards
Individual standard is the output expected from an average-worker under average working conditions for a given period of time.
Generally, individual standards are fixed for all employees in the organization, especially at the lowest level.
The individual standard of a worker is the output which he must produce in a fixed period of time. In other words, it is the time given to him for producing one unit of output.
For example, a performance standard may be four units per hour or 15 minutes per unit. Both are the same. So, a worker who is doing packing-work may be asked to pack four products per hour. In other words, he is given 15 minutes to pack a single product.
Therefore, an individual standard is a fixed number of products, which must be generated by a worker in a fixed-period. That is, it is the fixed-output of the worker per unit of time.
Individual standard also has other names like labor standard, employee standard, employee time standard, or time standard.
The concept of individual standards in terms of production is depicted below.
Image credits © Prof. Mudit Katyani.
2. Departmental Standards
The company is divided into different departments. Each department is given a specific function or work to do. Standards are fixed for each department. Here, standards are fixed for quantity of output, quality of output, costs of output, etc.
A department consists of some individuals. Departmental standards are fixed by adding individual standards of each member of the department. A department's performance is judged based on these fixed standards.
For example: Assume, the standard output of the production department is 1000 units per day. If the production department produces exactly 1000 units per day, then it is 100% efficient. If it produces more than 1000 units, its efficiency is greater than 100%. If it produces less than 1000 units, then its efficiency is below 100%.
The manager of the department is responsible for getting the work done from his workers. He must see that all the work is done in accordance with departmental standards. He must see that all his department's objectives are achieved. He must try his level best to improve the team spirit in his department. He must also improve the co-ordination and co-operation in his department.
Concept of departmental standards in production terms is depicted below.
Image credits © Prof. Mudit Katyani.
3. Plant Standards
Plant standards are fixed for an entire plant or a factory. A plant is a place or location where goods are produced and/or assembled. It consists of that place where machines, equipments, materials and workers interact with each other, directly or indirectly, with an intention to produce goods.
Plant standards are fixed for:
- Total output in quantitative and qualitative terms.
- Various cost in the production process.
The output depends on the level of technology, the type of employees and the estimated demand for the product.
Plant standards mean to fix the output to be produced for a given period. Here, both quantitative and qualitative output is fixed. The pant standard must be realistic. In other words, it must not be very high or too low. Generally, it is based on the output produced in the past. However, necessary adjustments are made for future demand of the product.
Various costs are involved in the production of goods, namely;
- Labor costs.
- Material costs.
- Overhead costs.
Plant-standards also mean to fix the standard labor, material and overhead costs. After manufacturing a product, the actual labor, material and overhead-costs are compared with the standard-costs. After comparison, the difference found is noted down. Further, the reasons why this difference occurred are also looked upon. After this, the difference is corrected to minimize the cost in the future. Every organization wants to reduce its costs. However, costs reduction must never be done by compromising the quality of the produced goods.
The concept of plant standards in terms of production is depicted below.
Image credits © Prof. Mudit Katyani.
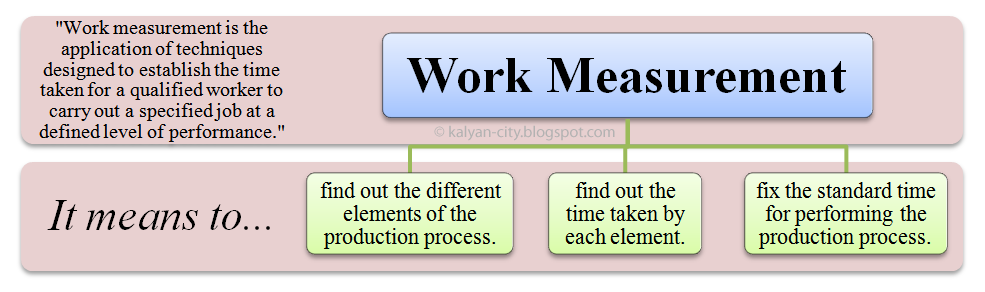
Work Measurement - Definition Meaning Purpose Objectives
Definition of Work Measurement
According to International Labour Organization
“Work measurement is the application of techniques designed to establish the time taken for a qualified worker to carry out a specified job (task) at a defined level (rate) of performance.”
International Labour Organization (ILO) stated this important definition of work measurement in its publication.
Now let's proceed to know the meaning of work measurement.
![square]() Meaning of Work Measurement
Meaning of Work Measurement
The meaning of work measurement is mainly based on three key steps.
Work measurement means to:
- Find out the different elements (parts) of the production process (job).
- Find out the time taken by each element.
- Fix the standard time for performing the production process.
For example, publishing a book is a production process. There are many elements, which are involved in the publication of a book. In other words, book publication involves production steps like typing a manuscript, editing the written matter, proof reading it, followed by printing and binding.
Work measurement involves finding out the time taken for doing each element. The time taken for each element is totaled. This is the standard time for publishing the book. Here, provisions are also made for relaxation, breakdown of machines, etc.
![square]() Purpose of Work Measurement
Purpose of Work Measurement
The uses, importance, objectives or purpose of work measurement data:
The main purpose of work measurement:
- Manpower planning.
- Production planning and scheduling.
- Estimating productions costs.
- Cost reduction and control.
- Rational basis for incentives.
- Performance appraisal.
- Training of employees.
- Comparing alternative methods.
- Accepting new orders.
- Fixing the selling cost.
Now let's discuss, "What work measurement is used for?"
1. Manpower planning
Work measurement data is used for manpower planning. This is because it gives information about the total hours required to perform the job. This helps to estimate the number and type of employees who are required to do the job. It ensures that there will not be any excess staff.
Work measurement data also helps to estimate the number of machines and equipment that will be required in the future. This helps to find out the number of employees who will be required to handle these machines and equipment.
2. Production planning and scheduling
Work measurement data is used for production planning and scheduling. This is because this data is used for making production standards. This data is also used for scheduling. Scheduling means to fix starting and finishing time for each job. This cannot be done without work measurement data.
3. Estimating productions costs
Work measurement data helps to estimate the production cost. This is because it gives management accurate data about production time. This data helps to estimate the labor costs. Secondly, indirect costs such as fuel and power consumption, rent and salaries of staff, etc. also depends on the production time factor.
4. Cost reduction and control
Work measurement data is used to reduce and control costs. It helps to reduce the labor cost. This is because it provides a guideline to the employees to work efficiently and effectively. This helps to make optimum use of the available manpower. So the labor cost will reduce.
Work measurement data helps to reduce material costs. It also helps to increase machine productivity. All these steps help to reduce and control production costs.
5. Rational basis for incentives
Work measurement data is used for making incentive schemes for the employees. Incentive schemes motivate employees to work hard. The efficient employees are rewarded by giving them a higher wage rate.
Work measurement fixes the standard-time for doing the work. Those who complete their work within a standard time or faster than the standard-time are rewarded with higher wages. This encourages all employees to work fast and efficiently.
6. Performance appraisal
Performance appraisals are done to find out whether the employees are efficient or not. It is done to find strengths & weaknesses of employees.
Work measurement helps to do performance appraisals. This is because it fixes the standard-output and standard-time for each employee. The employees who produce the standard-output within the standard-time are efficient and vice versa. Thus, it also helps to find out the strengths and weaknesses of the employees.
7. Training of employees
Work measurement helps to train the employees, especially the new employees. It divides the full job into small elements (parts). It gives complete details about each element of the job. It gives details about; how to do each element, the time taken for each element, the machines and tools involved in each element, etc. These details are used for training the employees.
8. Comparing alternative methods
There are many methods for doing a job. Work measurement data helps to choose the best method for doing a job.
9. Accepting new orders
Work measurement data tells us when will each job be completed. So, it helps the company to decide whether to accept new orders or not. In other words, it helps to find out whether the new-order will be completed within a specific time limit.
10. Fixing the selling cost
Work measurement data also helps to fix the selling cost of product. This is because it estimates the cost of production, especially the labor cost. Selling cost is decided after fixing the estimated production cost.
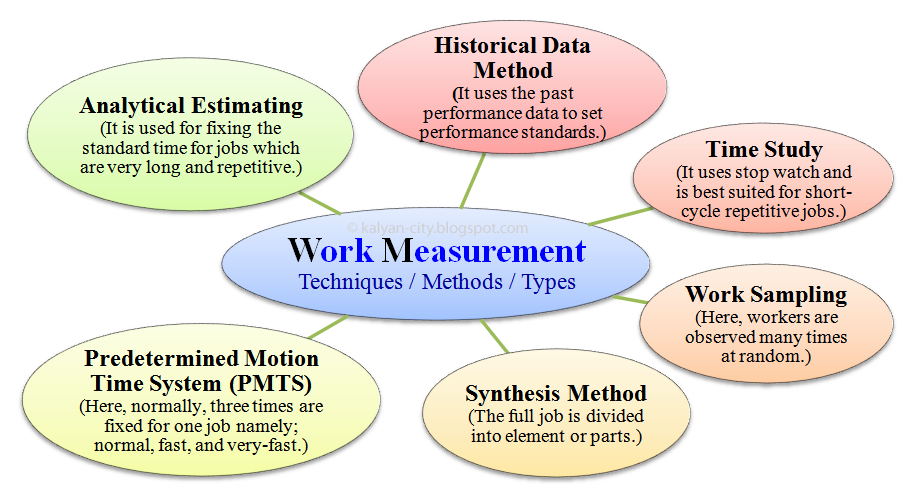
Work Measurement Techniques Methods Types
Work Measurement Techniques
Image depicts different work measurement techniques, methods or types.
Work measurement techniques are listed below:
- Historical data method - It uses the past performance data to set performance standards.
- Time study - It uses stop watch and is best suited for short-cycle repetitive jobs.
- Work sampling - Here, workers are observed many times at random.
- Synthesis method - Here, the full job is divided into element or parts.
- Predetermined motion time system (PMTS) - Here, normally, three times are fixed for one job namely; normal, fast, and very-fast.
- Analytical estimating - It is used for fixing the standard time for jobs, which are very long and repetitive.
Now lets discuss more above techniques of work measurement.
1. Historical data method
Historical data method uses the past-performance data. Here, past performance is used as a guideline for setting work performance standards. The main advantage of this technique is that it is simple to understand, quicker to estimate and easier to implement. However, past performance is not the best basis for fixing performance standards. This is because there may be many changes in technology, employees behavior, abilities, etc.
2. Time study
Time study with the help of a stop watch is the most commonly used work measurement method. This technique was developed by Frederick Winslow Taylor (1856-1915).
Time study is best suited for short-cycle repetitive jobs. Most of the production jobs can be easily timed by a time-study.
Time study procedure consists of the following steps:
- Select the job to be timed.
- Standardize the method of doing the job.
- Select the worker to be studied.
- Record the necessary details of the job and conditions of work.
- Divide the job into elements. Here, element is a part of the job.
- Find out the time taken to do every single element.
- Keep provisions for relaxation, etc.
- Fix the standard time for doing the job.
3. Work sampling
Work sampling method was original developed by Leonard Henry Caleb Tippett (1902-1985) in Britain in 1934. In this technique, the workers are observed many times at random. It is done to find out for how much time the worker is actually on the job. It checks how long he is working and how much time he is not working (idle time).
Work sampling method does not involve stop watch measurement. The purpose of work sampling technique is to estimate what proportion of a workers time is devoted to work-related activities.
Work sampling method involves following three main steps:
- Deciding what activities are defined as working. Non-working are those activities which are not defined as working.
- Observe the worker at selected intervals and record (write down) whether he is working or not.
- Calculate the portion of time (P), a worker is working.
A portion of time (P) a worker is working equals to Number of observations during which working occurred divided by Total Number of observations.
The above calculation is used as a performance standard.
To know more, read advantages and disadvantages of work sampling.
4. Synthesis method
In synthesis method, the full job is first divided into elements (parts). Then the time taken to do each element of the job is found out and synthesized (totaled). This gives the total time taken for doing the full job. In this technique, the time taken to do each element of the job is found out from previous time studies. So, this technique gives importance to past-time studies of similar jobs. It also uses standard data.
Standard-data is the normal time taken for doing routine jobs. Standard data is easily available for routine-jobs like fitting screws, drilling holes, etc. So there is no need of calculating these times repeatedly. Most companies use Standard-data. They do not waste time doing studies for all elements of the job. This is because standard time is already available for most elements of a job.
For example, a job of publishing a book contains four elements viz; typing, editing, printing and binding. The time taken for doing each element is first found out. Suppose, typing takes 40 days, editing takes 30 days; printing takes 20 days and binding takes 10 days. Then the time taken to do all the elements are totaled. That is, it takes 40 + 30 + 20 + 10 = 100 days to publish a book. This information is taken from previous time studies of other printing jobs or from the standard data.
Synthesis technique also considers the level of performance. Level of performance refers to the speed of performance, which is either, normal, fast, or very-fast.
The benefits or advantages of synthesis method:
- It provides reliable information about standard time for doing different jobs. This is because it is based on many past time studies.
- It is economical because there is no need to conduct new time studies.
5. Predetermined motion time system
In Predetermined Motion Time System method or simply PMTS technique, the normal times are fixed for basic human motions. These time values are used to fix the time required for doing a job. Normally, three times are fixed for one job. That is, one time is fixed for each level of performance. The level of performance may be normal, fast and very-fast.
PTMS is better than motion studies because it gives the detailed analysis of the motion, and it fixes the standard time for doing that motion.
PTMS technique is used mostly for jobs, which are planned for future. However, it can also be used for current jobs as an alternative to time study.
The benefits or advantages of PMTS method:
- It is a very accurate method. It avoids subjective judgement or bias of rater.
- It is an effective and economical method for repetitive jobs of short duration.
- There is no interference in the normal work routine, and so it does not face any resistance from the employees.
- It helps to improve the work methods because it gives a detailed analysis of the motions.
- It is more economical and fast compared to normal time studies.
6. Analytical estimating
Analytical estimating method or technique is used for fixing the standard time for jobs, which are very long and repetitive. The standard-time is fixed by using standard-data. However, if standard data is not available, then the standard time is fixed based on the experience of the work-study engineer.
The benefits or advantages of analytical estimating technique:
- It helps in planning and scheduling the production activities.
- It provides a basis for fixing labor rate for non-repetitive jobs.
- It is economical because it uses standard data for fixing the standard time of each job.
One disadvantage or limitation of analytical estimating method:
- When standard-data is not available for a job, then the standard time is fixed by the work-study engineer. He uses his experience and judgement for estimating the standard-time. This is not accurate compared to a scientific time study.
So, these are different techniques of work measurement.
 Importance of Advertising
Importance of Advertising